There Needs to Be Improved QC for Protein Reagents
Introduction
Proteins and peptides represent the most widely utilized research reagents and they are frequently employed in various therapeutic and diagnostic applications. In addition, proteins are also utilized to provide insights of functional mechanisms in structural biology, antibodies generation, cell biology experiments, chemical biology, genomics tools and microscopic assays1. In order to utilize protein reagents for desired applications, there is urgent requirement of improved quality control (QC) in terms of purity, production and reproducibility. Quality control of protein reagents deemed essential for precise measurement system and ensures reproducibility over time under different operating conditions.
Despite of utilization of purified proteins in various research domains, quality control of protein reagents is not much explored and currently there are no clear standard or guidelines available to follow. The utilization of proteins and peptides are often restricted in therapeutics due to inadequate protein quality and poor data reproducibility. Moreover, there is a vast impact on both the quality and cost of research through usage of poor-quality peptides, proteins and antibodies as experimental reagents. As per statistics, a staggering economic cost of $28 billion per annum in the US alone is imposed with 50 percent irreproducible preclinical experiments from 2012 research data. Out of this $28 billion per annum economic burden, approximately $10.4 billion which equates to 36% is attributed to poor quality biological reagents and reference materials2. In biomedical research, ability to utilize protein reagents identical to published research work is central to reproducibility. However, serious flaws in protein reagents quality and reproducibility of experimental data presents alarming situation to not only pharmaceutical industries but also to scientific community. Nevertheless, improved quality control of protein reagents is pertinent to ensure identification of poor protein quality and limit irreproducibility. Currently, with the increased awareness about the lack of reliability and reproducibility of protein reagents, there are few journals wherein authors are asked to include the quality control data of protein reagents in their studies3. Pharmaceutical industries generally keep a tab on quality control of reagents through highly regulated and controlled processes, however; there is no clear guidelines or standards in place in the academic research to ensure high protein quality. Consequently, there is urgent requirements of defined set of guidelines for the scientists, reviewers, editors and funding agencies to provide more reliable experimental data using protein reagents.
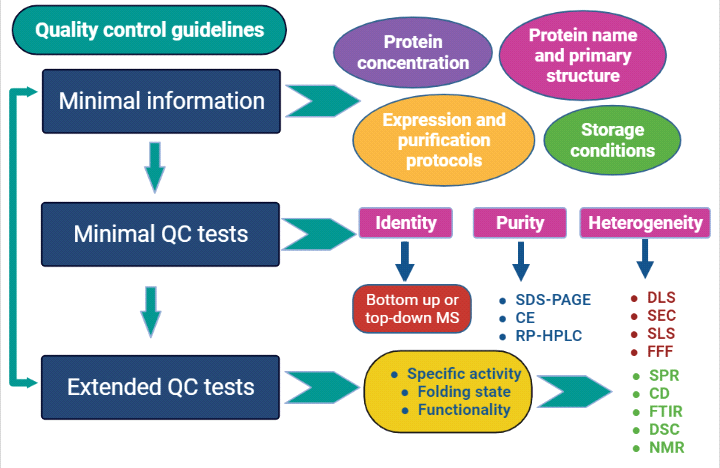
In order to address this obvious imbalance and the problem of data reproducibility when protein reagents are involved, a working group comprising of The Association of Resources for Biophysical Research in Europe (ARBRE-MOBIEU) and the Production and Purification Partnership in Europe (P4EU) laid down a list of recommended quality control guidelines to aid in the validation of high-quality protein samples being used in biological, biophysical and biochemical research4. The implementation of guidelines for protein quality evaluation should be considered as an entry point towards the development of improved quality control of protein reagents. The developed guidelines based on earlier available literature and extensive professional experience of a wide community of specialists from ARBRE-MOBIEU and P4EU for the quality control of protein reagents mainly comprises of three parts viz., minimal information, minimal QC tests, and extended QC tests.
1. Minimum information
Minimum information represents a list of sufficient information that should be provided in publications related to protein identity, expression and purification parameters. This information can be employed for reproducibility of experimental data in any laboratory.
- Protein concentration quantification method should be provided along with storage conditions (for ex., buffer composition, pH, temperature, freezing or lyophilization techniques, wherever applicable).
- Detailed description of expression and purification protocols along with complete storage conditions should be made available in case of recombinant proteins to accurately reproduce the results in any laboratory.
- Complete sequence of amino acids of the final protein after cloning and expression should be given along with detailed cloning strategies to avoid unnecessary production trials.
2. Minimal Testing
Minimal QC tests comprises of simple widely available experimental methods to be tested on protein samples such as identity, purity, homogeneity, activity, and time stability and storage. These minimal QC tests provides reliable indicators regarding quality of protein being employed as reagents for yielding high reproducibility of experimental results.
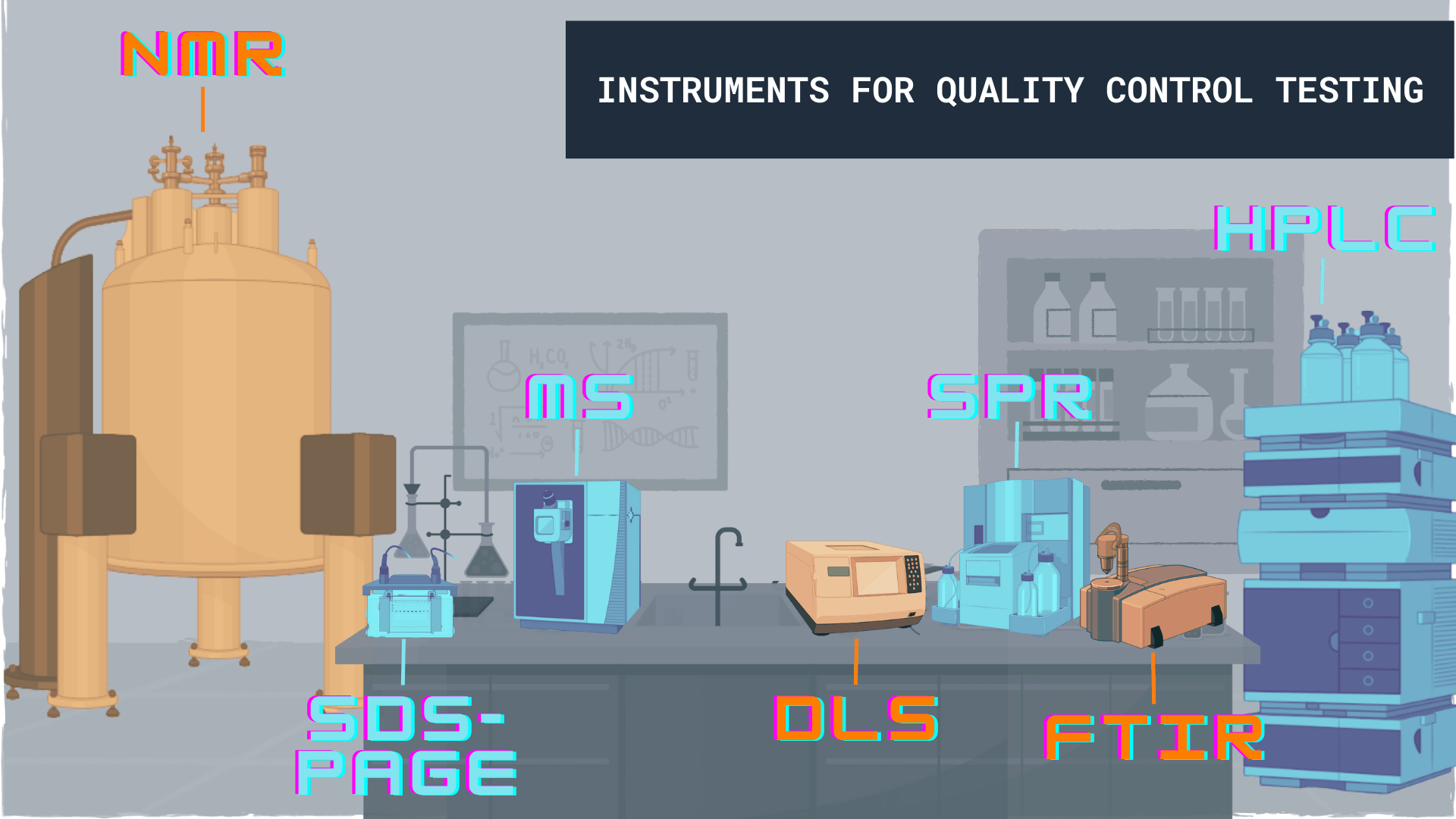
- Identity of protein samples should be preferably confirmed using either “bottom up” mass spectrometry (MS) (mass fingerprinting or tryptic digest) or “top down” mass spectrometry (by checking intact protein mass)5. “Bottom-up” MS identify the correct protein without any contamination. On the other hand, “top-down” MS confirm the identity of protein with information about intactness/micro-heterogeneity indicating whether proteolysis happened during purification or not. Other complementary method includes Edman sequencing.
- Purity of protein samples should be assessed by using SDS-PAGE, capillary electrophoresis or Reversed-Phase-HPLC (RP-HPLC)6. These methods are being utilized to detect presence of any potential contaminants, proteolysis events etc. In addition to these methods other complementary method namely isoelectric focusing (IEF) should be employed to distinguish the protein of interest from closely related undesired products.
- Homogeneity/monodispersity represents the size distribution of the protein sample and provide information regarding tendency to form aggregates or oligomeric state (monomer, dimer etc.). Polydispersity does not reflect protein instability, however the values less then 20% of dispersity (value of 0.2 and below) deemed acceptable in experimental set ups. Heterogeneity/aggregation can be preferable checked using Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) and/or Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC). Other complementary methods include Size Exclusion Chromatography in combination with Multi Angle Light Scattering (SEC-MALS), static light scattering (SLS), Field Flow Fractionation (FFF), or Field Flow Fractionation in combination with Multi Angle Light Scattering (FFF-MALS) or Analytical Ultracentrifugation (AUC).
3. Extended QC tests
The extended QC tests establish suitability of protein samples such as experimental reagents and are generally considered complementary in addition to the minimal QC tests. These tests are highly recommended for further characterization of proteins (folding state and specific activity) utilized in specific experimental downstream applications. Active and functional status of proteins are confirmed by measuring the activity of protein samples after homogeneity assessment.
- The methods utilized for activity determination includes active concentration measurement using Surface plasmon resonance (SPR), and total concentration measurement using Bradford, bicinchonic acid or Lowry assays. The extended quality control tests include general quality testing by UV spectroscopy, protein competent fraction (specific activity) determination using surface plasmon resonance (SPR) technique, conformation/folding state determination using Fourier Transform InfraRed (FTIR), Circular Dichroism (CD), Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, endotoxin/lipopolysaccharides content analysis and batch to batch consistency assessment. In addition, extended QC tests include homogeneity assessment using complementary methods such as analytical Ion Exchange Chromatography (IEC), analytical Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography (HIC) or Isoelectric Focusing (IEF).
Taken together, the ability to reliably reproduce the experimental data as well as the confidence level in the published data employing protein reagents would significantly improve with the proposed list of recommended QC guidelines.
References
____________________________________________________________________________________________
- Raynal B, Lenormand P, Baron B, Hoos S, England P. Quality assessment and optimization of purified protein samples: why and how? Microbial Cell Factories 2014; 13:180.
- Freedman, LP, Cockburn, IM, Simcoe TS. The economics of reproducibility in preclinical research. PLoS Biol. 13, e1002165 (2015).
- Reproducibility: let’s get it right from the start. Nat. Commun. 9, 3716 https:// doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06012-8 (2018).
- de Marco A, Berrow N, Lebendiker M, Garcia-Alai M, Knauer SH, Lopez-Mendez B, Matagne A, Parret A, Remans K, Uebel S, Raynal B. Quality control of protein reagents for the improvement of research data reproducibility. Nat Commun. 2021 May 14;12(1):2795. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23167-z.
- Tipton JD, Tran JC, Catherman AD, Ahlf DR, Durbin KR, Kelleher NL. Analysis of intact protein isoforms by mass spectrometry. J Biol Chem 2011, 286:25451–25458.
- Fekete S, Veuthey JL, Beck A, Guillarme D. Hydrophobic interaction chromatography for the characterization of monoclonal antibodies and related products. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2016; 130:3-18.