Biosimilars: Navigating the Landscape for Future Therapeutics
Abstract:
Biosimilars, a burgeoning field within the pharmaceutical industry, hold immense promise in revolutionizing the accessibility and affordability of biologic medicines. This article explores the complexities of biosimilars, including their development process, regulatory challenges, economic impact, and future prospects. By delving into these intricacies, we aim to provide valuable insights for commercial biopharmaceutical and academia researchers navigating the dynamic landscape of biosimilars.
Introduction:
In the rapidly evolving landscape of pharmaceuticals, biosimilars stand out as a key player poised to transform the availability and affordability of biologic medications. A biosimilar medication is a biological product highly similar to an already approved biologic drug, also known as the reference product. Biosimilars hold significant importance in healthcare, offering a potential solution to the rising costs associated with biologic therapies. By fostering competition and expanding patient access, biosimilars have the capacity to reshape the treatment paradigm for various diseases, including cancer, autoimmune disorders, and chronic conditions.
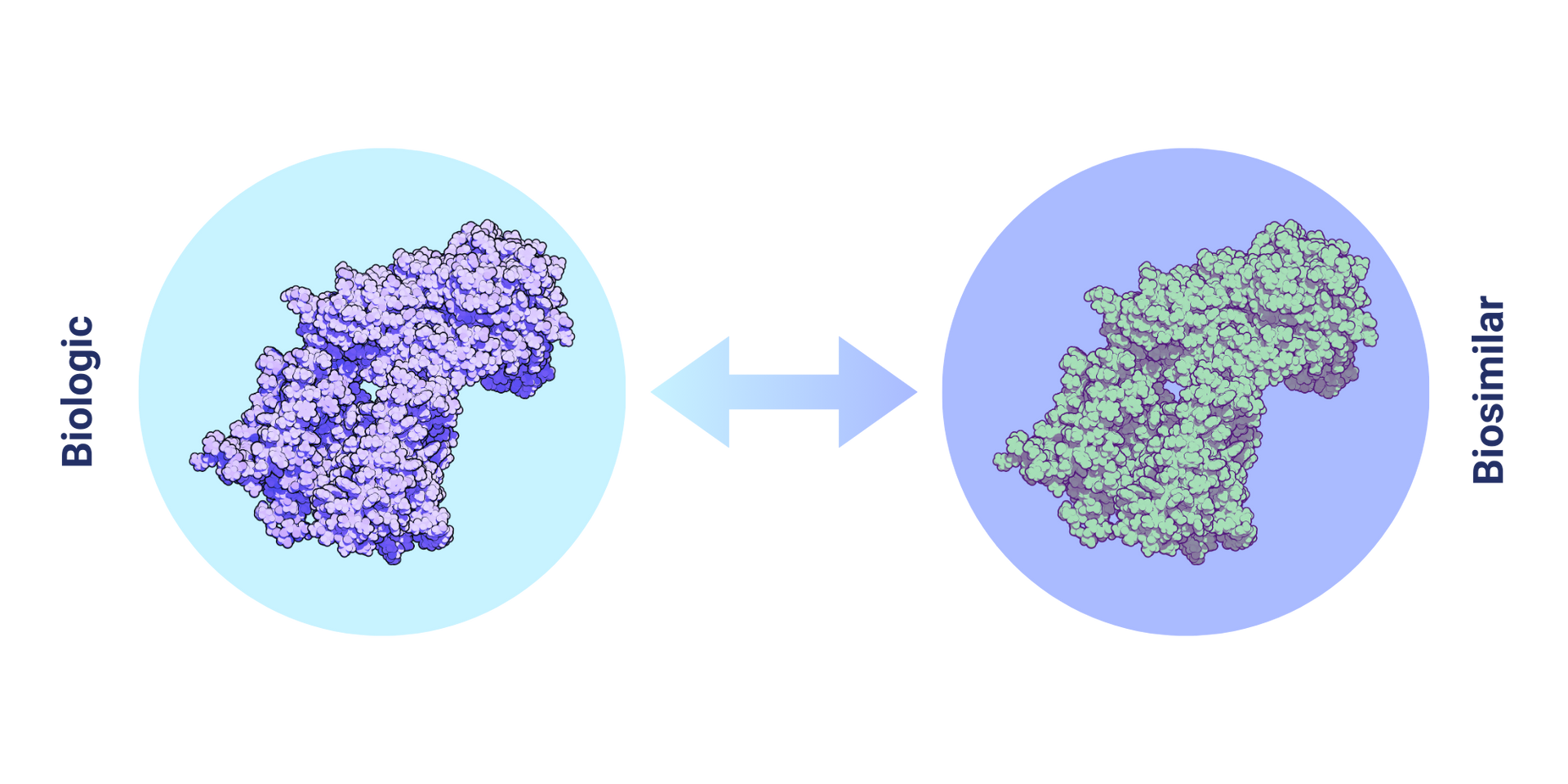
What is a Biosimilar Medication?
Biosimilars are biologic drugs that are highly similar to their reference products, with no clinically meaningful differences in terms of safety, purity, and potency. Unlike generic drugs, which are chemically synthesized and exact copies of their branded counterparts, biosimilars are produced through living organisms and exhibit inherent variability due to their complex molecular structure. Despite this variability, biosimilars undergo rigorous analytical and clinical testing to demonstrate similarity to the reference product, ensuring their efficacy and safety.
Understanding Biosimilars
The development of biosimilars requires a deep understanding of the underlying science behind biologic drugs and their replication. Unlike small-molecule generic drugs, which can be precisely replicated, biosimilars face challenges due to the complexity of biologic molecules and their manufacturing processes. Biosimilars must demonstrate similarity in physicochemical characteristics, efficacy, and safety through comprehensive comparative studies, including analytical characterization and clinical trials. By leveraging advanced biotechnology techniques, developers strive to achieve biosimilarity while maintaining therapeutic equivalence with the reference product.
Development Process of Biosimilars
The journey from conceptualization to commercialization of biosimilars involves navigating a complex development process. This process encompasses several stages:
- Molecular Characterization: The development begins with comprehensive analysis of the reference product's molecular structure to identify critical attributes.
- Non-clinical Studies: Preclinical studies evaluate the pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and toxicology of the biosimilar candidate, establishing its safety profile.
- Clinical Trials: Clinical trials are conducted to demonstrate equivalence in safety, efficacy, and immunogenicity compared to the reference product
- Analytical Characterization: Extensive analytical testing is conducted to assess physicochemical properties, purity, and potency, ensuring biosimilarity
- Comparative Studies: Comparative clinical studies are conducted to establish similarity in efficacy and safety profiles between the biosimilar and reference product
The development of biosimilars is fraught with challenges, including variability in manufacturing processes, ensuring comparability, and addressing immunogenicity concerns. These challenges can be overcome through rigorous analytical characterization, robust clinical trial design, and collaboration with regulatory authorities to establish appropriate standards and guidelines. Additionally, fostering transparency and communication with healthcare providers and patients is essential to build trust and confidence in biosimilar therapies.
Economic Impact of Biosimilars
Biosimilars have the potential to significantly impact healthcare costs by fostering competition and expanding market access. Studies have shown that the introduction of biosimilars can lead to substantial cost savings, making biologic therapies more affordable for patients and healthcare systems.
- In Europe, the introduction of biosimilars for infliximab resulted in significant cost savings for healthcare systems and patients, particularly in the treatment of autoimmune diseases.
- Similarly, in the United States, the availability of biosimilars for filgrastim led to reduced healthcare expenditures and increased access to treatment for patients with cancer undergoing chemotherapy.
These case studies illustrate the market impact of biosimilars and their role in driving down prices, increasing treatment accessibility, and promoting sustainability in healthcare systems. As biosimilar adoption continues to grow, their economic implications will become increasingly pronounced, reshaping the pharmaceutical market dynamics.
Challenges in the Biosimilars Market
Despite their potential benefits, biosimilars face several challenges in the market landscape. Intellectual property issues and patent litigation can impede biosimilar market entry, delaying competition and limiting patient access. Moreover, market acceptance varies among healthcare providers and patients, influenced by factors such as perception of efficacy, safety concerns, and brand loyalty. Addressing these challenges requires collaboration among stakeholders to foster education, promote trust, and enhance awareness of biosimilars' value proposition.
Opportunities & Future Prospects
The growing role of biosimilars in global healthcare systems presents numerous opportunities for innovation and access. Future trends in biosimilar development, including the emergence of biosimilars for complex biologics and personalized therapies, hold promise for expanding treatment options and improving patient outcomes. Strategies for successful biosimilar implementation encompass regulatory compliance, market access initiatives, and stakeholder engagement. By embracing these opportunities and overcoming challenges, biosimilars have the potential to revolutionize healthcare delivery and enhance patient care worldwide.
Conclusion
In conclusion, biosimilars represent a transformative force in the pharmaceutical landscape, offering a pathway to increased accessibility and affordability of biologic therapies. By navigating the complexities of biosimilar development, regulatory approval, and market acceptance, researchers and stakeholders can unlock the full potential of biosimilars to address unmet medical needs and improve patient outcomes. As we embark on this journey towards a future shaped by biosimilars, collaboration, innovation, and patient-centricity will be essential in realizing their promise. Embracing biosimilars as a catalyst for change, we pave the way for a more equitable and sustainable healthcare ecosystem.
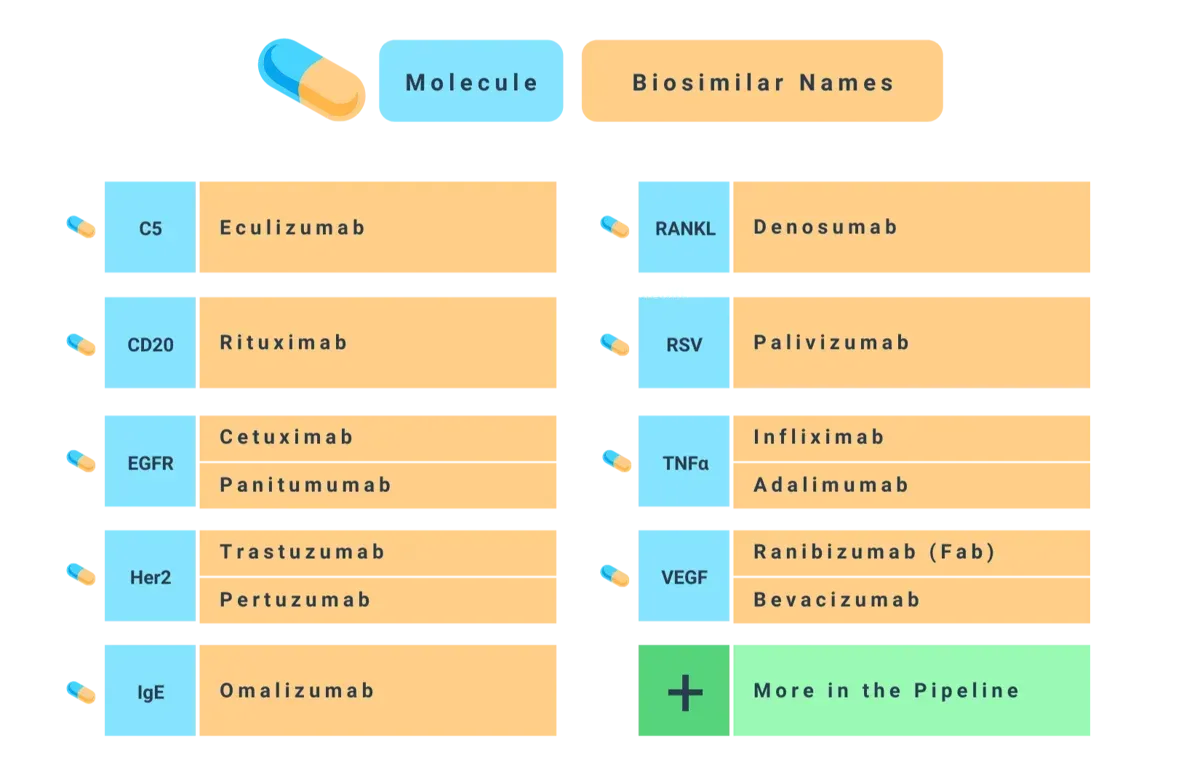
Biosimilars and kbDNA
kbDNA offers a competitive library of biosimilars, and the expertise needed to navigate the world of biosimilars. Contact us today if you need help finding a particular item, if you have questions, or to tell us what specific parameters you’re looking for in your biosimilars. You can also request a spec sheet for any of our biosimilars.
For our expert help with custom tailored reagents, oligo-nucleotide synthesis services, or to further discuss the role of biosimilars in your research and within kbDNA, contact us today. Let's push the boundaries of scientific exploration together.